Hey everyone! If you’re new to AI and wondering what all the buzz is about, you’re in the right place. In this tutorial, we’ll break down the basics of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in simple terms. No prior tech knowledge required, we’ll start from scratch and build up. By the end, you’ll understand key concepts, real-world examples, and even how to dip your toes into AI yourself.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
AI is essentially the simulation of human intelligence in machines. It’s about creating systems that can perform tasks that typically require human smarts, like recognizing speech, making decisions, or playing games.
Types of AI
Fun fact: The term “AI” was coined in 1956 at the Dartmouth conference, kicking off decades of research.
1. AI types based on Capabilities:
This classification focuses on the scope of intelligence, from task-specified to superhuman.
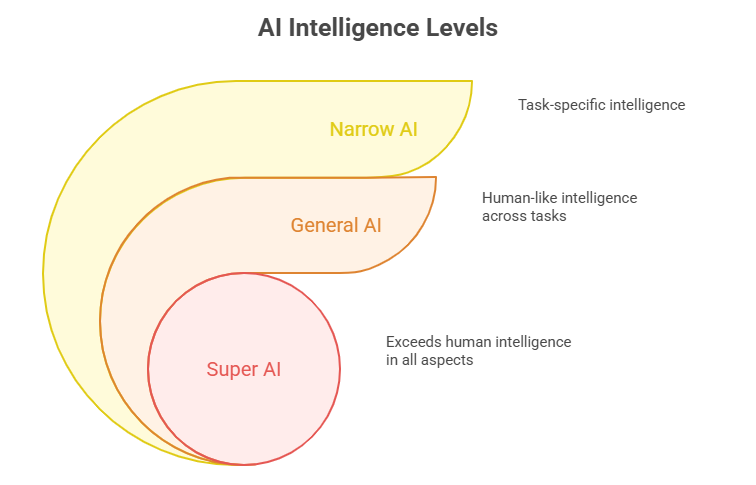
| Category | Description | Examples |
| Narrow AI (Weak AI) | This is the AI we see today. It’s designed for specific tasks. It doesn’t “think” like a human-it’s just really good at one thing. | Virtual Assistants like Siri or Google home Recommendation algorithms on Netflix or Instagram and more |
| General AI (Strong AI) – AGI | This is sci-fi level stuff, where machines can understand, learn, and apply knowledge across any task, just like humans. We’re not there yet! | Hypothetical; no true examples exist yet. Concepts appear in research prototypes or sci-fi (e.g, JARVIS from IRON MAN) OpenAI aim toward this. |
| Super AI (ASI) | Even further out – AI that surpasses human intelligence in every way. | Skynet from Terminator or Chitti from Enthiran Movie (but hopefully friendlier). Purely theoretical; could lead to breakthroughs or risks. |
2. AI types Based on Functionality
AI systems can be grouped according to how they handle information, make choices, and interact with their surroundings. This approach highlights the progression from basic response mechanisms to advanced cognitive abilities. Below is an overview of the primary categories, presented in a table for easy reference. These are drawn from established frameworks in the field, but explained here in straightforward, original terms.
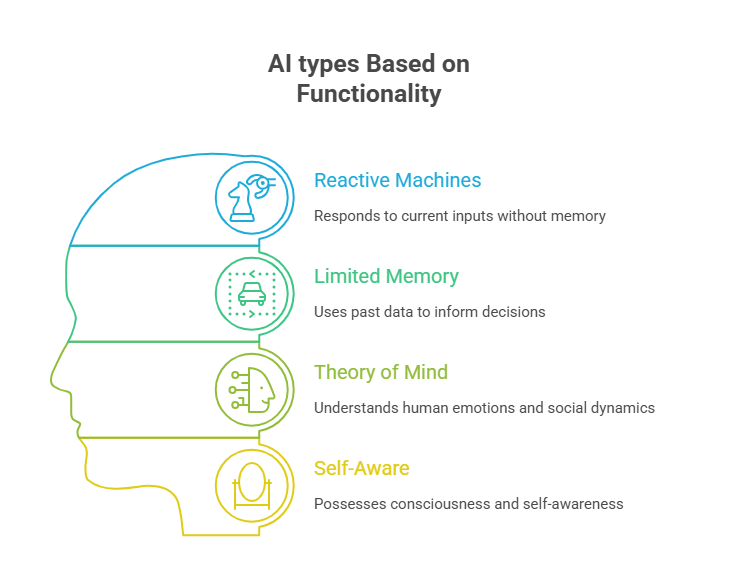
| Category | Description | Examples |
| Reactive Machines | These AIs focus solely on the present moment, reacting to inputs without storing or learning from previous encounters. | Board game opponents like the one in chess software that evaluates moves instantly. |
| Limited Memory Systems | Building on reactive ones, these incorporates historical data to refine their actions and predictions. They “remember” patterns from training to handle dynamic situations better. This is the foundation for much of today’s practical AI. | Autonomous vehicles that analyze road data from sensors and past trips to avoid obstacles. |
| Theory of Mind Systems | A more sophisticated level where AI grasps concepts like emotions, intentions, and social cues in other. This enables nuanced interactions, anticipating how people or other systems might respond. Currently, this remains largely in development stages. | Experimental companion robots designed for elderly care that detect mood through facial expressions and adjust conversations accordingly. |
| Self-Aware Systems | The pinnacle of functionality, where AI develops a sense of its own existence, goals, and internal states-essentially a form of consciousness. This could lead to independent decision-making beyond human programming. It’s still hypothetical and sparks ethical debates. | No real-world instances yet; but conceptual ideas include advanced sci-fi scenarios. |
How Does AI Work?
AI isn’t magic—it’s built on data, algorithms, and computing power. Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Data: The fuel for AI. Machines learn from vast amounts of information, like images, text or numbers.
- Algorithms: Step-by-Step instructions that tell the machines how to process data. For example, a sorting algorithm organizes a list.
- Machine Learning (ML): A Subset of AI where systems improve from experience without being explicitly programmed. Think of it as teaching a kid to ride bike-they get better with practice.
- Deep learning: A type of ML using neural networks (inspired by the human brain) to handle complex tasks like image recognition.
Key AI Techniques
| Technique | Description | Example Application |
| Rule-Based Systems | Follows pre-defined rules set by humans. | Chess program like early Deep Blue. |
| Machine Learning | Learn patterns from data. | Spam filters in emails. |
| Neural Networks | Layers of interconnected nodes mimicking brain neurons. | Facial recognition in phones. |
| Natural Language Processing (NLP) | Handles human Language. | Chatbots like Chatgpt, Grok, Deepseek and more. |
Real-World Examples of AI
AI is everywhere- here are few everyday uses:
- Healthcare: AI analyzes X-rays to detect diseases faster than doctors in some cases.
- Transportation: Self-driving cars from companies like Tesla use AI to navigate roads.
- Entertainment: Algorithms on Spotify curate playlists based on your listening habits.
- Business: Predictive analytics helps companies forecast sales or detect fraud.
Note: AI isn’t perfect-it can have biases if trained on flawed data. Always think critically about its outputs!
Why Learn AI Now?
AI is transforming jobs, industries, and society. Learning it can open doors to careers in tech, data science, or even creative fields like AI art. Plus, understanding AI helps you navigate ethical questions, like privacy concerns or job automation.
If this sparked your interest, stay tuned for Part 2: Diving into Machine Learning!






